Microscopy Guide
Master the art of microscopy with our comprehensive guides and tips.
1. Choosing Your Microscope
Selecting the right microscope depends on what you want to observe. Here's a breakdown to help you pick the perfect tool for your application.
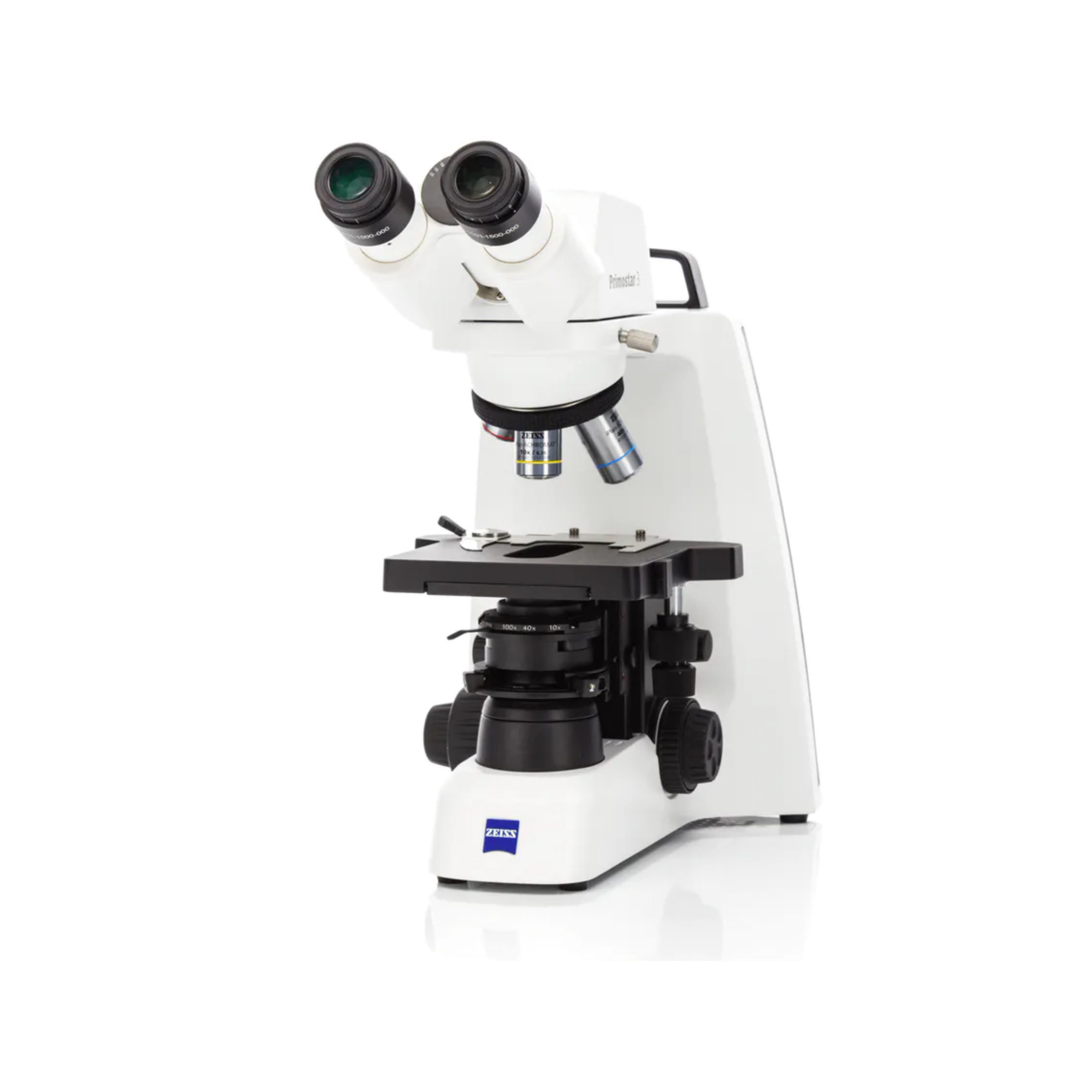

🔬 Biological Microscope
Ideal for live cell imaging, tissue sections, and bacteria. Uses transmitted light to reveal structures inside transparent samples.
Example: Axio Lab.A1, Primostar 3

✨ Fluorescence Microscope
Ideal for molecular labeling and protein tracking. Uses high-intensity light to excite fluorescent dyes.
Example: Axio Imager 2, Axio Observer
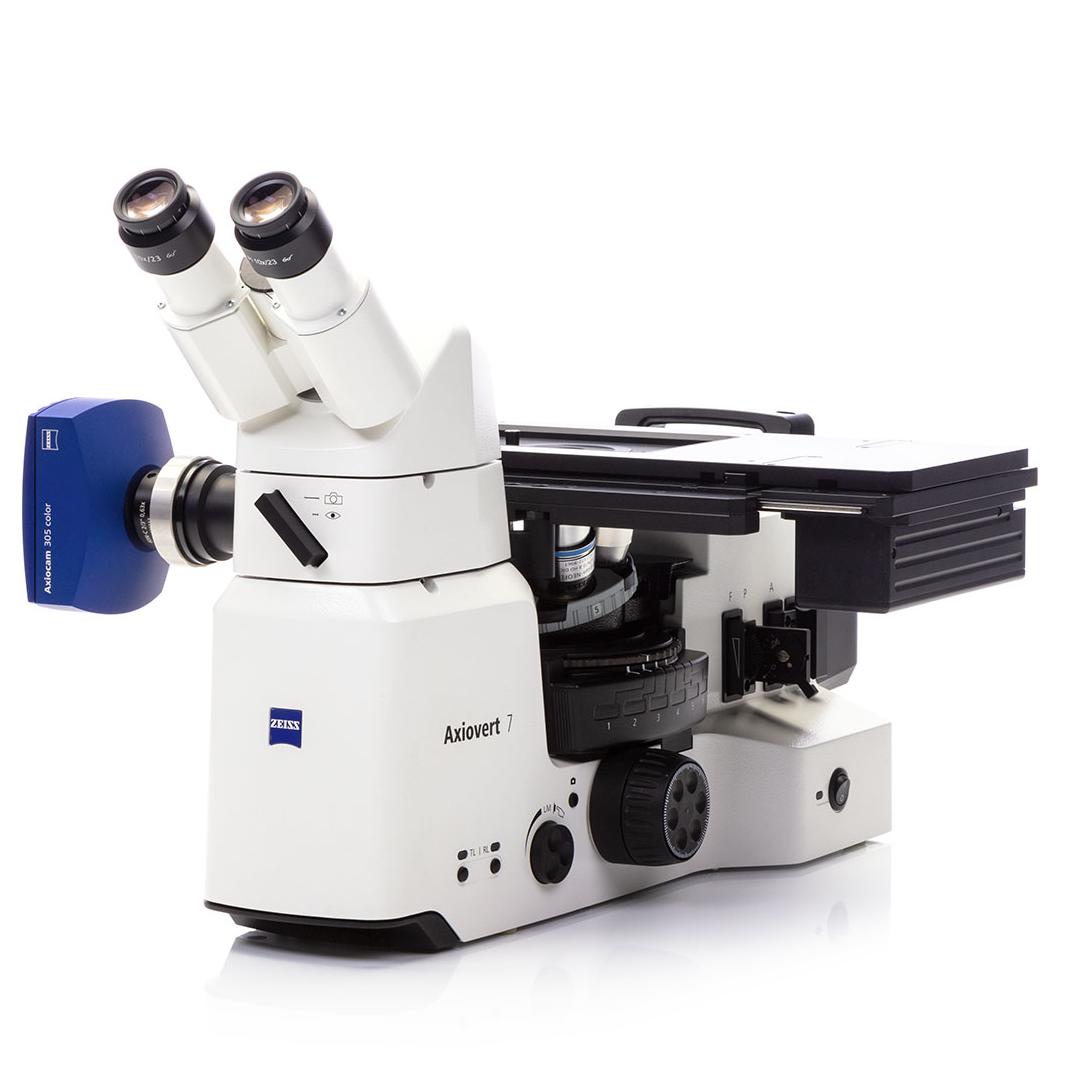
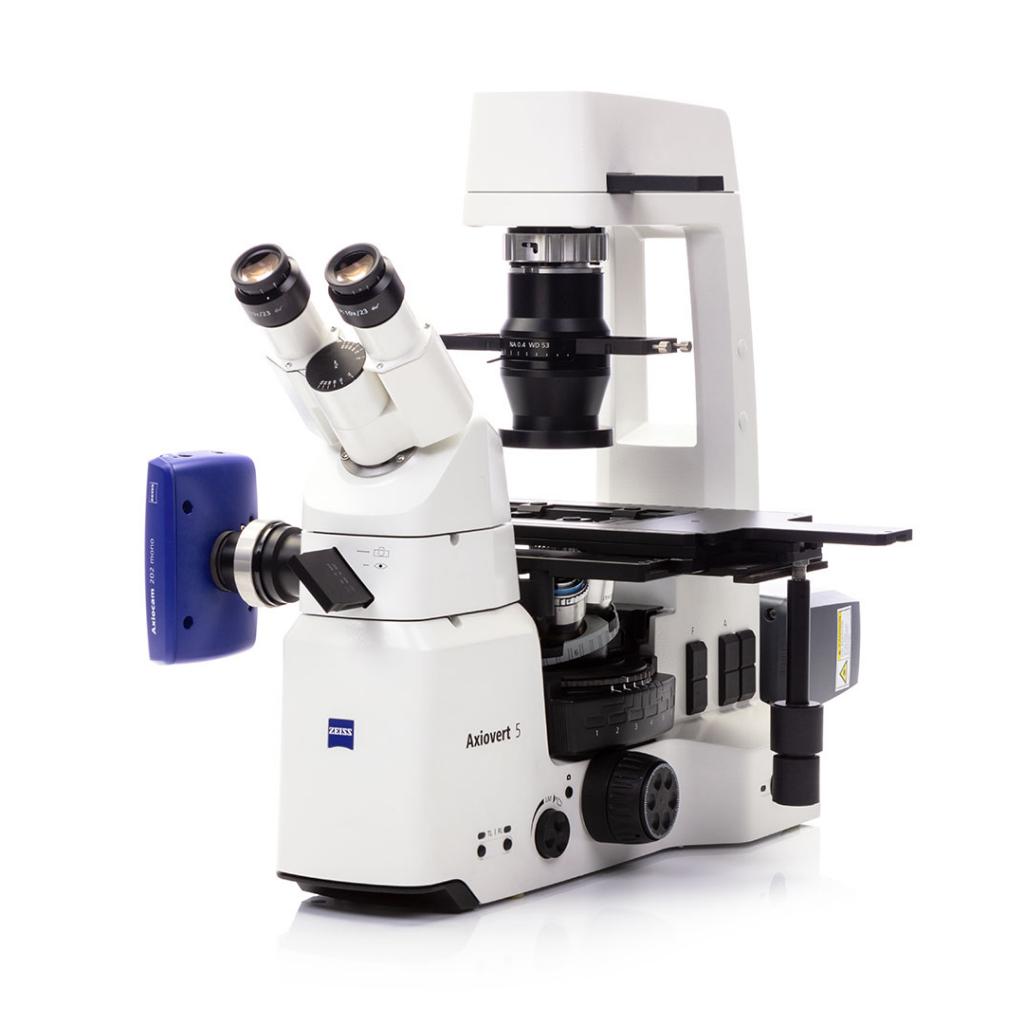
🛠️ Metallurgical Microscope
Ideal for surface inspection of opaque materials like metals and composites using reflected light.
Example: Axio Scope.A1 MET
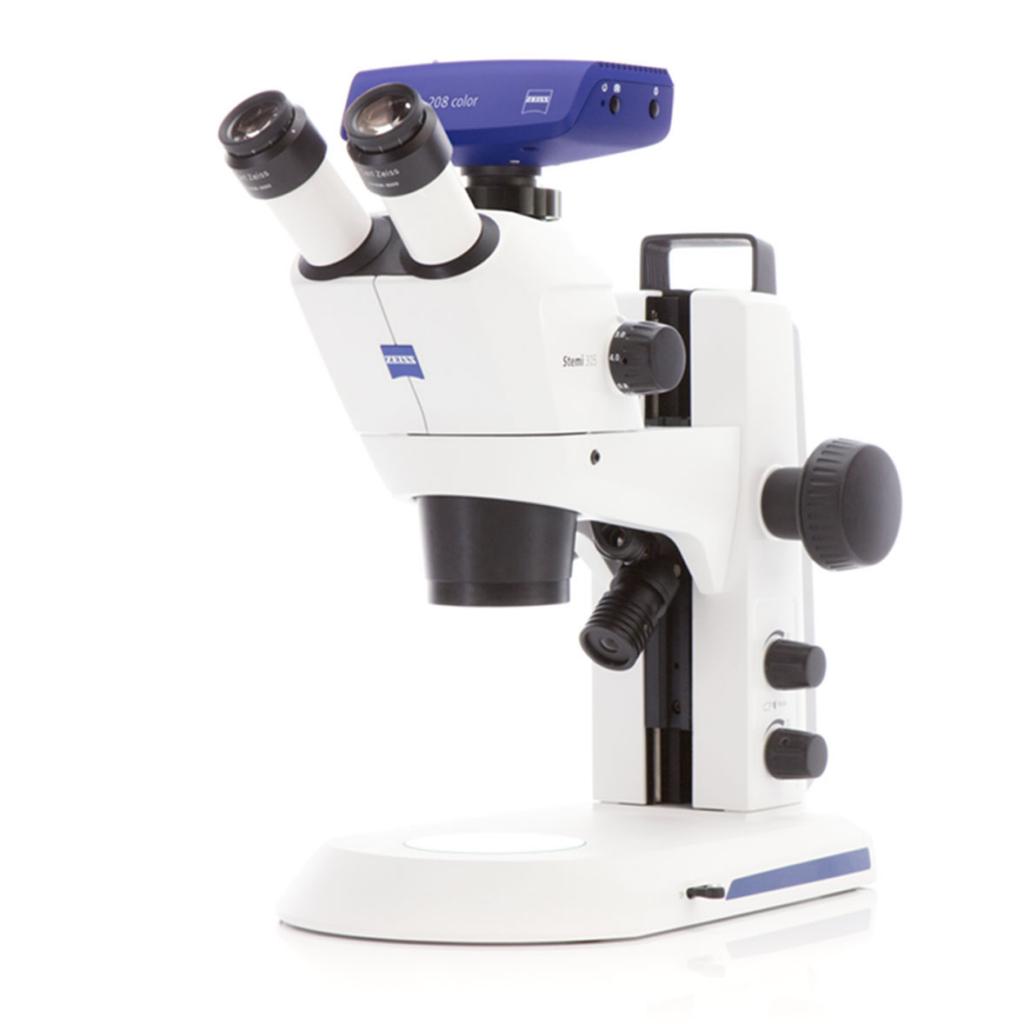

🧠 Stereomicroscope
Ideal for 3D observation, soldering, and dissection. Offers wide field of view and depth perception.
Example: Stemi 305, Stemi 508
2. Technical Tips & Best Practices
Fluorescence Optimization
- Minimize Phototoxicity: Use the lowest possible excitation intensity to keep cells healthy.
- Signal-to-Noise: Use cooled monochrome cameras (e.g., Axiocam 202 mono) for detection of faint signals.
- Multichannel: Ensure flat-field correction is active for uniform illumination across all channels.
Image Stitching
- Overlap: Maintain 10-15% overlap between tiles for seamless merging.
- Shading Correction: Essential to remove vignetting at tile edges before stitching.
- Hardware: A motorized stage is highy recommended for precise, automated acquisition.
Live Cell Imaging
- Environment: Strictly maintain 37°C, 5% CO₂, and high humidity to prevent evaporation.
- Focus Strategy: Use "Definite Focus" or predictive autofocus to counter thermal drift.
- Speed vs. Quality: Prioritize frame rate and low exposure over high resolution to capture dynamics.
Maintenance
- Optics: Clean oil objectives immediately after use with lens tissue and spark plug cleaner (or approved solvent).
- Calibration: Recalibrate scaling using a micrometer slide if you change objectives or cameras.
- Storage: Cover the microscope when not in use to protect coatings from dust accumulation.